What Is a Cash Dividend?
A cash dividend is a sum of money that is distributed to stockholders typically from the company’s current profits or cumulative gains.
Unlike stock dividends or other forms of value payments, cash dividends are paid out in full. Reinvesting or accepting cash dividends are the two options most brokers provide.
- A cash dividend is a distribution of cash, rather than stock or any other kind, that a company makes to its shareholders on a regular basis.
- Cash dividends are sometimes given out as one-time payments, like following a settlement, but they are also frequently paid on a regular basis, like monthly or quarterly.
- You can choose to accept or reinvest cash dividends from most brokers.
- Usually, dividend-paying businesses are well-established, have consistent cash flow, and have progressed past the growth stage.
- Plans for reinvesting dividends (DRIPs) are becoming more and more popular among brokers and corporations.
How a Cash Dividend Works
Companies often use cash dividends as a means of giving back capital to their shareholders on a quarterly basis, though certain stocks have the option to pay these bonuses on a monthly, annual, or semiannual basis.
Even though many businesses pay dividends on a regular basis, some only pay out special cash dividends to shareholders in response to one-time, nonrecurring events like lawsuit settlements or loans for sizable one-time cash distributions. Every business sets its own dividend policy and reviews it every so often to determine whether to reduce or increase dividends. Cash dividends are paid on a per-share basis.
The Timing of Cash Dividends
On a declaration date, the board of directors of the company announces a cash dividend, which entails paying a specific amount per common share. Following that notification, the record date—the day on which a company ascertains which of its shareholders are eligible to receive the payment—is set.
Furthermore, an ex-dividend date is set by stock exchanges or other relevant securities organizations and is usually two business days prior to the record date. Investors who purchased common stock prior to the ex-dividend date are eligible to receive the declared cash dividend.
Dividend earnings are taxable as income for the recipients and must be reported by investors. The total amount of reportable dividend earnings is listed on IRS Form 1099-DIV.
Which Companies Pay Dividends?
Dividend-paying companies usually have steady cash flows and are established businesses that have moved past the growth stage. This business growth cycle helps to explain why growth companies don’t pay dividends since they require the money to grow their operations, construct factories, and hire more staff.
Some companies that distribute dividends could even set dividend payout targets based on the profits they made in a particular year. For instance, banks usually distribute cash dividends, which represent a specific portion of their profits. The dividend policy may be changed or delayed until a better time if profits fall.
One popular method used by businesses to give capital back to shareholders is cash dividends.
Accounting for Cash Dividends
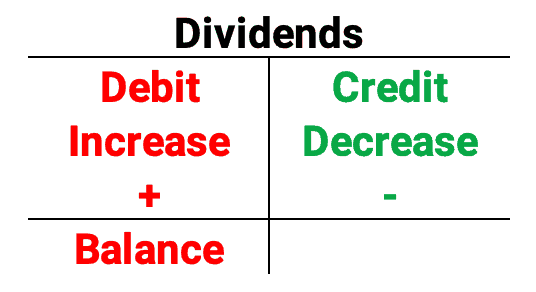
A company credits a liability account known as dividend payable and debits its retained earnings when it declares a dividend. The business credits its cash account for the corresponding cash outflow and reverses the dividend payable with a debit entry on the date of payment.
Cash dividends do not affect a companys income statement. But they also reduce a company’s cash balance and shareholders’ equity by the same amount. Any cash dividend that a company pays out must be included in the financing activity section of the cash flow statement.
The trailing 12-month (TTM) dividend yields, which are calculated by dividing a company’s dividends per share for the most recent 12-month period by its current stock price, are the simplest way to compare cash dividends across companies. This calculation standardizes the cash dividend measure in relation to the share price.
Cash Dividend Example
Rather established, Nike distributes cash dividends on a quarterly basis. In February 2022, the sportswear brand announced a $0. 305 per share quarterly cash dividend payable Apr. 1, 2022. The company reported year-over-year (YOY) growth in revenues of 19% for the fiscal year 2021. 3%. Meanwhile, earnings per share (EPS) rose 123%.
What Is a Stock Dividend?
Stock dividends, which are less common than cash dividends, provide shareholders with extra shares of stock as payment.
What Is a Special Dividend?
Outside of the regular dividend schedule, shareholders receive a special dividend. It could be the consequence of a spin-off, windfall profits, or other unusual business move. Special dividends are typically larger than regular dividends but are nonetheless uncommon.
What Are Dividend Aristocrats?
A stock is considered a dividend aristocrat if its dividend has increased for at least 25 years in a row. Examples include AT&T, ExxonMobil, Caterpillar, 3M, and IBM, among others. Article Sources: Investopedia mandates that authors cite original sources to bolster their claims. These consist of government data, original reporting, white papers, and conversations with professionals in the field. When appropriate, we also cite original research from other respectable publishers. You can read more about the guidelines we adhere to when creating impartial, truthful content in our
FAQ
Why are dividends debited?
Since cash dividends are paid from retained earnings, the journal entry would show a credit to dividend payable and a debit to retained earnings. It’s critical to understand that the payment date marks the actual cash outflow.
What type of account is dividends?
The cash and shareholder equity accounts are the main targets of a cash dividend. After dividends are paid, there isn’t a separate balance sheet account for them. Nevertheless, the business records a liability to shareholders in the dividends payable account following the dividend declaration but prior to the actual payment.
Do dividends go up with debit or credit?
Are dividends paid a debit or credit in the trial balance?
Response and explanation: Paid dividends have an impact on trial balance because they cause the income statement’s cash flow to decline. But this creates a credit on the dividends that must be paid, and the trial balance shows this.
Read More :
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/cashdividend.asp