Secured Debt vs. Unsecured Debt: An Overview
There are two primary categories of consumer financing options that include loans: secured debt and unsecured debt. The main distinction between the two is whether or not collateral is there to safeguard the lender in the event that the borrower defaults.
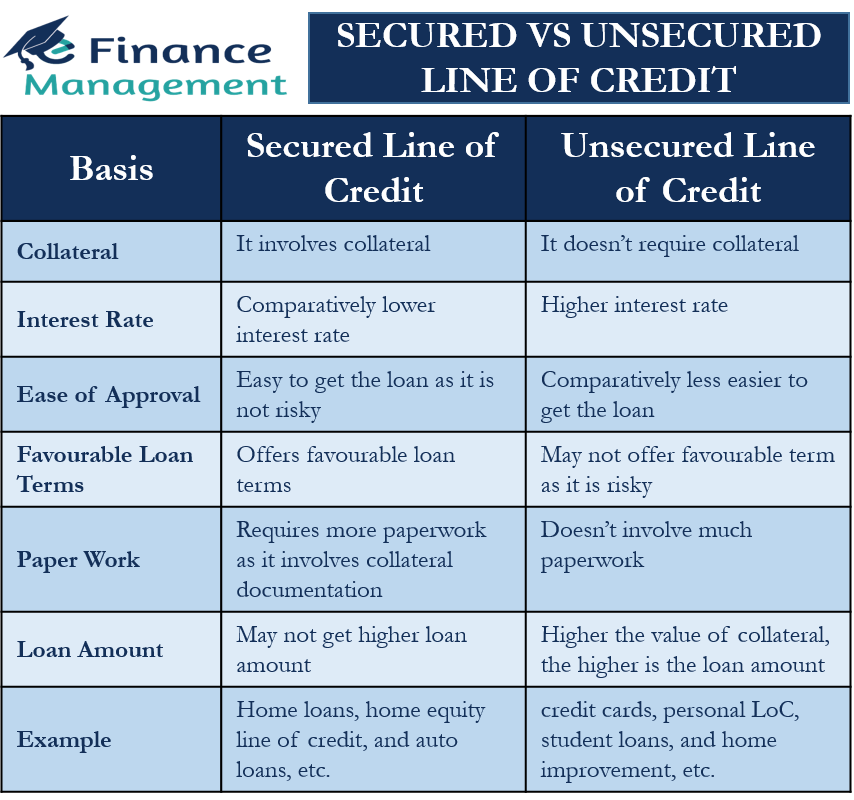
- Debts classified as secured are ones for which the borrower pledges an asset as security for the loan.
- The secured loans lower the amount of risk for lenders.
- Unsecured debt has no collateral backing.
- An unsecured loan’s funding is provided by lenders exclusively on the basis of the borrower’s creditworthiness and repayment commitment.
- Interest rates on secured debt are typically lower because the lender is not as risk-averse.
What Is Secured Debt?
Debts classified as secured are ones for which the borrower pledges an asset as security for the loan. A secured debt simply means that the lender has the right to take possession of the asset in order to recoup the money it advanced to the borrower in the event of default.
Mortgages and auto loans are common examples of secured debt for consumers; in these cases, the object being financed serves as collateral for the financing. If the borrower on a car loan defaults on the loan, the loan issuer may eventually take possession of the vehicle. A mortgage is secured by the property that is taken out by an individual or business. Until the mortgage is fully repaid, the lending institution retains equity (financial interest) in the property. The lender may seize and sell the property to recover all or a portion of the money owed in the event that the borrower defaults on the payments.
An additional form of secured debt that is likewise secured by the borrower’s home is a home equity loan or home equity line of credit (HELOC). If a homeowner has enough equity, they can simultaneously hold a conventional mortgage and a home equity loan, or HELOC, on the same asset.
Similar to this, companies can obtain secured loans and use cash, invoices, capital equipment, real estate, or inventory as collateral.
Secured loans typically have more lenient credit requirements than unsecured loans because of their lower risks. For instance, 620 is typically regarded as sufficient credit for a conventional mortgage, and the government-insured Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loans have an even lower cutoff point of 500. However, just like with unsecured loans, the higher your score, the more money you might be able to borrow or the lower your interest rate might be.
Collateral, or anything used as security against loan non-repayment, is the main distinction between secured and unsecured debt.
What Is Unsecured Debt?
As the name suggests, unsecured debt is not backed by collateral and does not require any security. When a borrower defaults on this kind of debt, the lender has to file a lawsuit to attempt to recoup its losses.
All that matters to lenders when issuing an unsecured loan is the borrower’s creditworthiness and commitment to repay. As a result, the interest rates that banks charge on these so-called signature loans are usually higher. Additionally, these loans typically have stricter requirements regarding debt-to-income ratios and credit scores, and only the most qualified applicants are granted access to the funds. Although certain personal loans are accessible to individuals with lower credit scores, obtaining a wide variety of advantageous personal loans usually requires a credit score of at least 670.
But if you can fulfill the strict requirements, you might be able to get approved for the greatest personal loans out there.
Unsecured debts, apart from bank loans, comprise unpaid medical bills, some retail installment contracts, like gym memberships, and the remaining balances on the majority of credit cards. The credit card company is effectively providing you with a line of credit with no collateral requirements when you obtain a piece of plastic. However, in order to offset the risk, it charges high interest rates on any money you borrow.
An unsecured debt instrument, such as a bond, has a higher level of risk than its counterpart, the secured bond, because it is backed only by the creditworthiness and dependability of the issuing company. Interest rates on unsecured debt are typically higher because the lender is at a greater risk than with secured debt.
Unsecured government debt can be a special case. For example, U. S. Despite being unsecured, government-issued Treasury bills, or T-bills, have cheaper interest rates than a lot of other debt instruments. This is because there is essentially no default risk associated with this type of debt instrument because the government can print more money or impose taxes to cover its obligations.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-difference-between-secured-and-unsecured-debts.asp-final-c2040f78625b44d98372ea024fa51697.png)
Advantages of Secured and Unsecured Debt
Even though the advantages of each form of debt have already been covered, let’s go over them in more detail.
Pros of Secured Debt
Here are the advantages of secured debt:
- Lenders feel more secure knowing that collateral, like real estate or valuable assets, is present. This implies that you’ll likely receive a lower interest rate.
- Your monthly payments with secured debt may be slightly lower because interest rates are probably lower.
- Because the secured asset helps verify the possibility of future debt payments, secured loans are frequently easier to obtain, especially for those with poorer credit scores or shorter credit histories.
- Lenders may be willing to grant longer payment terms for secured debt because the secured asset protects their interests. This implies that consumers’ monthly cash flow may be slightly less of a strain.
Pros of Unsecured Debt
Here are the advantages of unsecured debt:
- People who take out unsecured loans don’t have to worry about losing particular assets in the event of default because they don’t require collateral.
- The absence of collateral could simplify the application procedure and expedite approvals. This is due to the lack of evidence that any assets are being secured.
- Borrowers who take out unsecured loans typically have the freedom to use the money however they see fit. On the other hand, secured loans could be connected to the underlying asset (i.e. e. To purchase a car, the secured asset, a car loan is required.
Unsecured Loans With Favorable Terms
Well-qualified borrowers may occasionally be granted an unsecured loan with advantageous terms that are closer to those of a secured loan.
Using this method, lenders evaluate a borrower’s income, reputation, credit history, and financial standing before making a loan decision. But unlike secured loans, there isn’t any down payment required for collateral attached to physical assets like real estate or cars. The lender is still prepared to offer advantageous conditions and interest rates, for instance, in light of the standing and stability of the company. The lender is agreeing to favorable terms even though this is an unsecured loan (often reserved only for secured loans)
This strategy is especially beneficial for people who want favorable loan terms without having to risk any particular assets. Since the lender is offering advantageous loan terms without having a secured asset to lower its risk exposure, this may be challenging to accomplish.
Secured Credit Cards
Be aware that a normally unsecured loan might occasionally be secured in the interim while the debtor establishes credit or strengthens their bond with a lender. One example of this is secured credit cards.
Credit cards that require a cash deposit from the cardholder as collateral are known as secured credit cards. If this sounds unfamiliar to you, it’s because most credit cards don’t usually require a secured asset. Upon issuance of the credit card, the credit limit is typically equivalent to the deposit amount.
A secured credit cardholder’s credit score can be improved by effectively managing the card, paying on time, and maintaining low balances compared to the credit limit. Furthermore, the card can become an unsecured line of credit by either requiring the surrender of the secured asset or granting more credit without one.
Secured and Unsecured Debt in Investing
Let’s briefly discuss the importance of secured and unsecured debt from the viewpoint of investors. You can invest in either secured or unsecured debt if you own bonds or corporate debt.
Risk diversification is advantageous for investors who hold both secured and unsecured debt in their portfolio, especially after learning that unsecured debt carries a higher risk. Although the risk of default is lower for secured debt that is backed by collateral, your potential return will also be lower due to the lower interest rates.
Theres also other investing things to keep in mind. For instance, as was previously indicated, secured debt might have longer terms. Because interest rates can fluctuate more over the long term than the short term, secured debt may put you at greater risk of interest rate fluctuations.
Which Is Better: Secured Debt or Unsecured Debt?
Because secured debt is less risky, it may be preferable from the lender’s perspective. Secured debt entails a risk for the borrower that, should they be unable to repay, they will have to give up their collateral. Positively, though, the interest rate will probably be lower than for unsecured debt.
Are Personal Loans Secured or Unsecured?
Although most people consider personal loans to be unsecured, they can actually be either Certain types of property, such as cars, boats, jewelry, stocks and bonds, life insurance policies, or cash in a bank account, could be pledged as security for a secured personal loan.
Does Secured Debt or Unsecured Debt Have Higher Rates?
Since unsecured debt is not supported by secured assets, it is riskier and frequently carries higher interest rates for borrowers.
Can I Combine Secured and Unsecured Debts?
Consolidating debts into a single, more manageable loan is known as debt consolidation. Borrowers may be able to reduce their overall interest expenses and streamline repayments by utilizing a secured loan (like a home equity loan) to settle high-interest unsecured obligations. People typically take this action to lower their interest costs and simplify their debt portfolio.
The Bottom Line
Loans may be secured or unsecured. Collateral is required for secured loans, and it can be anything of value—a home, a car, or another asset—that the lender can take back if the borrower defaults on the loan. Although collateral is not needed for unsecured loans, the borrower must still be deemed sufficiently creditworthy by the lender. Because they are viewed as less risky than unsecured loans, secured loans typically have lower interest rates. Article Sources: Investopedia mandates that authors cite original sources to bolster their claims. These consist of government data, original reporting, white papers, and conversations with professionals in the field. When appropriate, we also cite original research from other respectable publishers. You can read more about the guidelines we adhere to when creating impartial, truthful content in our
When you visit the site, Dotdash Meredith and its partners may store or retrieve information on your browser, mostly in the form of cookies. Cookies collect information about your preferences and your devices and are used to make the site work as you expect it to, to understand how you interact with the site, and to show advertisements that are targeted to your interests. You can find out more about our use, change your default settings, and withdraw your consent at any time with effect for the future by visiting Cookies Settings, which can also be found in the footer of the site.
FAQ
What is the most common form of unsecured credit?
A couple of the most prevalent forms of unsecured debt are credit cards and the majority of personal loans. There are ways to avoid this, even though lenders usually charge higher interest rates on certain kinds of debt. For example, you might be eligible for a credit card with a zero percent introductory rate.
Which type of credit is most likely to be unsecured brainly?
Answer. Credit cards are the kind of credit that are most likely to be unsecured.
What is an example of using unsecured credit?
unsecured loans include credit cards, personal loans, and student loans. If a borrower doesn’t make payments on an unsecured loan, the lender has the option of suing the borrower or hiring a collection agency to handle the debt collection.
Which type of that is often unsecured?
The two most popular types of unsecured loans are personal loans and credit cards. Credit lines of credit (LOCs) or unsecured loans are those in which lending takes place without the support of collateral with a comparable value.
Read More :
https://brainly.com/question/11321081
https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/110614/what-difference-between-secured-and-unsecured-debts.asp