A line of credit is a pre-approved loan that you can access incrementally rather than all at once. These credit lines frequently have flexible terms and are occasionally supported by an underlying asset, like a mortgage. A personal line of credit is typically unsecured, but a home equity line of credit (HELOC) is collateralized by a home.
If you need money, you can take out smaller amounts from a credit line or use the entire amount at once. Homeowners frequently use credit lines to finance renovations, making monthly payments to reduce the balance. Families sometimes use credit lines to fund more expensive vacations.
The majority of credit lines have a set borrowing and repayment period, usually between five and ten years. You have to pay off the remaining amount at the end of the term in order to renew the credit line with the new terms.
Lines of credit come in two forms: unsecured and secured. The first is totally dependent on your belief that you can pay back the loan. Lenders review your credit score, credit history, and provable income. The other secures the loan with an asset of comparable or higher value, such as your house or another type of property.
A line of credit gives you access to money “on demand” and can help you with expenses like a home project or unexpected car maintenance.
Lenders like banks and credit unions usually offer lines of credit, which allow you to access funds for a predetermined amount of time, provided you meet the eligibility requirements.
Only when you borrow money from the line of credit will interest be charged. Once you return borrowed funds, you can borrow that same amount once more. Here, flexibility is essential: as long as you follow the terms, which include repaying the loan in full and on time, you can decide when to withdraw the money, pay it back, and start again.
Continue reading to find out how credit lines operate and whether they’d be a good fit for you.
How do lines of credit work?
Let’s start by discussing your options if you need to borrow money. Generally speaking, you can apply for a credit line or a loan. When you take out a loan, you receive the money all at once and, regardless of when you use it, you have to pay interest right away.
A line of credit, on the other hand, provides you with a fixed amount of money that you can borrow as needed. But you don’t pay any interest until you actually borrow.
Although there are business credit lines, in this case we’ll focus on personal credit lines.
Most personal credit lines are unsecured, which means you can obtain one without pledging any collateral. Secured credit lines are guaranteed by assets like savings accounts or homes.
Higher credit scores may make you eligible for a lower annual percentage rate when you apply for a line of credit. Certain credit lines might have annual fees or borrowing limits in addition to other costs.
Following your approval for the line of credit, you will have a predetermined window of time (referred to as the “draw period”) during which you can withdraw funds from the account. A draw period can last several years. When you’re ready to borrow the money, the bank may give you special checks, a card to use, or transfer the funds to your checking account.
Interest typically begins to accrue as soon as you borrow money from your line of credit, and you’ll be required to make minimum payments, the amount of which will be added back to your available line of credit as you make them. However, after your draw period is over, you’ll go into the repayment period, during which you’ll have a deadline to settle any outstanding debt. Remember that paying the minimum amount due could result in higher interest over time.
How will a line of credit impact my credit scores?
Lenders may run a hard inquiry on your credit reports during the application process for a credit line. Your credit scores may momentarily drop as a result of this.
Generally, the line of credit shows up on your credit reports as a new account after you are approved and accept it.
Your credit scores may rise and your credit utilization rate may decrease if you never use the credit that you have available to you or use very little of it. The percentage of your available credit that you are currently using is indicated by your utilization rate. Your credit scores may suffer if you borrow a large portion of the line, as this could raise your utilization rate.
Also, if you make late payments, your credit may suffer.
Secured lines of credit
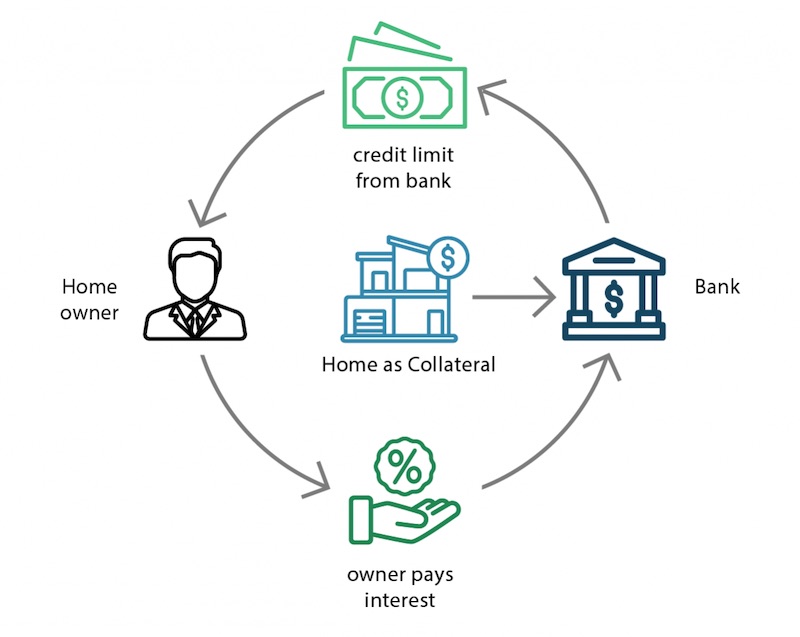
A home equity line of credit, or HELOC, is one choice if you’re looking to get a secured line of credit.
With a home equity line of credit (HELOC), you can borrow money against the equity that is currently there and use your house as collateral. They usually have a variable interest rate, so over time, your payments could go up.
Generally speaking, the bank will cap the amount you can borrow up to 85% of the appraised value of your home, less the remaining balance on your first mortgage. In addition to credit scores, banks consider your income and credit history when determining your interest rate.
If you don’t own a home or don’t want to use it as collateral, you might be able to obtain a line of credit secured by a certificate of deposit or savings account.
The drawback of a secured line of credit is that the lender may seize the asset used to secure the line if you are unable to make the payments.
Unsecured lines of credit
If you default on an unsecured line of credit, you might not lose your house or savings. However, the risk that the lender assumes when making an unsecured loan could result in higher interest rates than when making a secured line of credit.
Every unsecured line of credit has unique terms. The upper limit could be in the range of several thousand to several hundred thousand dollars. Certain credit lines have costs associated with them; for instance, you might have to pay an annual fee to maintain the account open.
What’s the difference between a credit card and a line of credit?
Credit cards are similar to lines of credit. Since both are revolving credit lines, you can take out as much as you want from them, pay them back (along with any interest you owe), and then borrow money again.
However, lenders offer credit cards and credit lines as two distinct products, and there are some important distinctions between the two.
There is no draw period associated with credit cards; you can use them for as long as the account is open and in good standing. Many have rewards programs, and if your card has a grace period and you can pay off your balance in full each month, you may be able to avoid paying interest altogether. This suggests that, when used sensibly, credit cards might be a better option for regular purchases.
The drawback of credit cards is that you might have to pay more to maintain a balance on one because they might have higher interest rates than lines of credit. Additionally, they might have lower limits than personal credit lines, and if you want to use a credit card cash advance to actually withdraw cash, you might have to pay hefty fees and annual percentage rates.
Tips for using a line of credit
Check your credit scores and take action to improve your credit health before taking out a line of credit, whether it be secured or unsecured, to increase your chances of being approved for a lower interest rate. Next, determine your financial needs and your intended course of action.
Bruce McClary, vice president of communications at the National Foundation for Credit Counseling®, advises asking for a line of credit if you require a flexible means of accessing funds.
However, he continues, “if you’re borrowing in an attempt to avoid getting into debt with another loan, there’s a deeper issue that needs to be addressed that can’t be addressed by borrowing more money.” ”.
Here are some recommendations for when to use a line of credit and when not to.
When not to use a line of credit
- A line of credit might not be the best option if you know you won’t be able to make the payments or if your income is erratic. It’s likely that your credit will suffer if you miss payments. Additionally, the collateral on a secured line of credit may be seized by the lender.
- Depending on your credit score, you might be able to find an unsecured personal loan with better rates than an unsecured line of credit if you know exactly how much you need and don’t want to use collateral.
- It may be a sign that you are having financial difficulties and shouldn’t take on more debt if you are using the line of credit for urgent needs or to cover transient costs like eating out and travel.
When to use a line of credit
- A home equity line of credit (HELOC) or secured line of credit may be a good option if you need the money for major expenses like schooling or home renovations, provided you have the funds to repay the loan. Bonus: You might be able to write off the interest you pay on the HELOC.
- Depending on the terms of each line of credit and your creditworthiness, an unsecured personal line of credit may help you avoid using collateral by allowing you to combine multiple small debts into a single payment with a lower APR.
FAQ
How do payments work on a line of credit?
Repaying a credit line You will receive a monthly statement that details the balance due on your credit line. You must make your minimum payment each month. Usually, your payment is equal to the monthly interest. But if you just pay the interest, you’ll never be able to settle your debt.
What are the downsides of a line of credit?
Usually, obtaining this fast credit is costly and time-consuming. You’re paying interest and initiation fees on money you didn’t need to borrow if you guess high. This reduces the efficiency of the entire investment and could be very problematic if the loan has early payoff penalties.
Is it a good idea to get a personal line of credit?
However, in general, it works best in circumstances where you have recurring costs and you might not be aware of the entire project’s cost, such as financing a new car, remodeling your kitchen, or encountering unforeseen medical or dental expenses. This is because the interest rate on a personal line of credit is usually lower than that of a credit card.
How does $1,000 line of credit work?
With a credit line, you can take out small loans, pay them back, and take out more as long as the line is available. Generally, the borrowed amount will incur interest while the line is available for borrowing; this distinguishes it from a traditional loan, which is paid back through predetermined installments.
Read More :
https://www.debt.org/credit/lines/